With the rapid increase in the number of urban vehicles, traditional parking lot management faces issues such as low efficiency and resource wastage. Ultrasonic sensors can significantly enhance parking efficiency and parking space management by monitoring real-time occupancy status.
Ultrasonic sensors operate on the principle of sound wave reflection. A transmitter emits high-frequency ultrasonic pulses, which reflect off obstacles (such as vehicles) and return to a receiver. By calculating the time difference for the sound waves to travel to and from an object, the system precisely measures distance.
When a vehicle enters a parking space, the sensor detects the change in distance and triggers a status update. This contactless measurement method avoids physical wear and is suitable for complex environments.
The smart parking system determines parking space status through preset thresholds. If the ultrasonic waves emitted by the sensor "pass freely" within the preset range, the space is identified as vacant. Conversely, if the ultrasonic waves are "blocked" within the preset range, the space is identified as occupied. The results are relayed in real-time via indicator lights (yellow for occupied, green for vacant) and a central display screen, ensuring both drivers and administrators can access the information promptly.
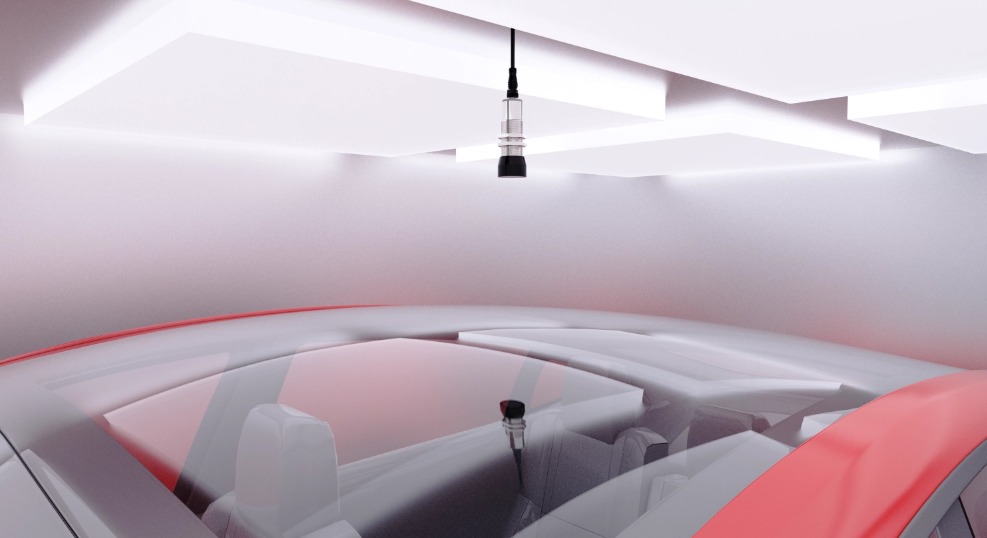

To address multi-path reflection interference caused by walls, ground surfaces, adjacent vehicles, etc., ultrasonic sensors not only require careful attention to installation positioning but also utilize core algorithms such as **time gating** and **beamforming** to minimize detection errors. When selecting sensors, it is advisable to opt for models with a **narrow beam angle** to avoid false detections resulting from an overly wide beam angle. Additionally, leveraging the **synchronization feature** of ultrasonic sensors ensures that even when installed side by side, they are not affected by each other’s emitted sound waves. By deploying multiple sensors to work collaboratively, false judgments due to other obstacles can be significantly reduced.
| Sensing range | 200-4000mm |
| Blind area | 0-200mm |
| Resolution ratio | 1mm |
| Repeat accuracy | ±0.15% of full scale value |
| Absolute accuracy | ±1% (temperature drift compensation) |
| Response time | 300ms |
| Switch hysteresis | 2mm |
| Switching frequency | 3Hz |
| Power on delay | <500ms |
| Working voltage | 9...30VDC |
| No-load current | ≤25mA |
| Output indication | Red LED: No target detected in teach-in state, always on; |
| Yellow LED: In normal working mode, the switch status; | |
| Blue LED: Target detected in teach-in state, flashing; | |
| Green LED: Power indicator light, always on | |
| Input type | With teach-in function |
| Ambient temperature | -25℃…70℃(248-343K) |
| Storage temperature | -40℃…85℃(233-358K) |
| Output characteristics | Support serial port upgrade and change the output type |
| Material | Copper nickel plating, glass bead filled epoxy resin |
| Protection degree | IP67 |
| Connection | 4 pin M12 connector/2m PVC cable |
Ultrasonic sensors, with their precision and reliability, have become a transformative force in modern garage management. Firstly, they optimize parking processes by reducing the time drivers spend searching for spaces, thereby enhancing user experience.
Secondly, through the integration of data from multiple sensors, smart parking systems enable the efficient allocation of parking resources. This approach also effectively reduces labor costs and improves operational efficiency. From enhancing daily parking efficiency to supporting macroscopic traffic planning, the application value of ultrasonic sensors is increasingly prominent, providing critical technical support for the long-term development of intelligent transportation systems.
Post time: Jan-20-2026